Welcome to the ultimate study guide for mitosis and meiosis! This comprehensive resource will guide you through the intricacies of cell division, providing an in-depth understanding of these fundamental processes.
From the meticulous stages of mitosis to the complexities of meiosis, this study guide unravels the mysteries of cell division, equipping you with the knowledge to excel in your studies and unlock the secrets of cellular life.
Mitosis
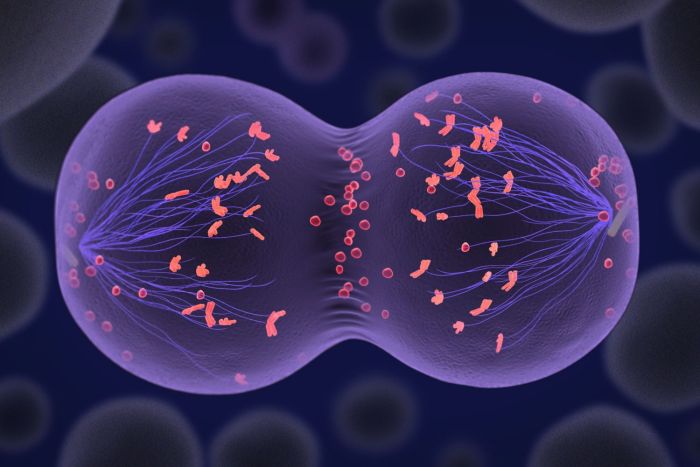
Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces two identical daughter cells from a single parent cell. It is a continuous process, but it can be divided into four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Stages of Mitosis
Prophase
- The chromosomes become visible.
- The nuclear envelope breaks down.
- The spindle fibers form.
Metaphase
- The chromosomes line up in the center of the cell.
- The spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes.
Anaphase
- The spindle fibers shorten, pulling the chromosomes apart.
- The chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell.
Telophase
- The spindle fibers disappear.
- Two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes.
- The cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two daughter cells.
Importance of Mitosis
Mitosis is essential for cell division and growth. It also plays a role in tissue repair and replacement. Mitosis ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes, which is necessary for the proper functioning of the cell.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Prophase | Chromosomes become visible, nuclear envelope breaks down, spindle fibers form |
| Metaphase | Chromosomes line up in the center of the cell, spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes |
| Anaphase | Spindle fibers shorten, pulling the chromosomes apart, chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell |
| Telophase | Spindle fibers disappear, two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes, cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two daughter cells |
Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell by half. This process is essential for sexual reproduction, as it ensures that each offspring receives the correct number of chromosomes from each parent.
Stages of Meiosis
Meiosis consists of two rounds of division, known as Meiosis I and Meiosis II. Each round of division is further divided into four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Meiosis I
- Prophase I:The chromosomes condense and become visible. Homologous chromosomes pair up and undergo crossing-over, exchanging genetic material.
- Metaphase I:The homologous chromosome pairs line up at the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase I:The homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase I:Two daughter cells are formed, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Meiosis II
- Prophase II:The chromosomes condense again.
- Metaphase II:The chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase II:The sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase II:Four daughter cells are formed, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Comparison of Meiosis Stages
| Stage | Meiosis I | Meiosis II |
|---|---|---|
| Chromosome number | Diploid (2n) | Haploid (n) |
| Number of divisions | One | One |
| Crossing-over | Yes | No |
| Independent assortment | Yes | Yes |
| Number of daughter cells | Two | Four |
Importance of Meiosis in Sexual Reproduction
Meiosis is essential for sexual reproduction because it ensures that each offspring receives the correct number of chromosomes from each parent. This is important because too many or too few chromosomes can lead to genetic disorders.
Meiosis also shuffles the genetic material of the parents, creating new combinations of genes in the offspring. This genetic variation is essential for evolution, as it allows populations to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis: Study Guide For Mitosis And Meiosis
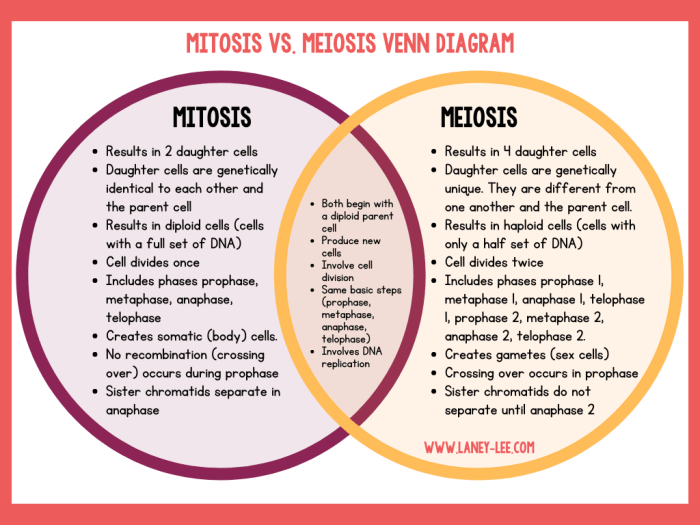
Mitosis and meiosis are two distinct types of cell division that occur in eukaryotes. While they share some similarities, they also have several key differences. These differences are due to the different functions of mitosis and meiosis in the life cycle of an organism.
Similarities between Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis and meiosis both involve the division of a cell into two daughter cells. In both cases, the DNA in the cell is replicated prior to division. The replicated chromosomes are then separated and distributed to the daughter cells. Mitosis and meiosis also both involve the formation of a spindle apparatus, which helps to separate the chromosomes.
Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis
The key differences between mitosis and meiosis are as follows:
- Number of daughter cells:Mitosis produces two daughter cells, while meiosis produces four daughter cells.
- Number of cell divisions:Mitosis involves one cell division, while meiosis involves two cell divisions.
- Chromosome number:The daughter cells of mitosis have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while the daughter cells of meiosis have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
- Genetic variation:Mitosis does not produce any genetic variation, while meiosis produces genetic variation through the process of crossing over.
| Characteristic | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Number of daughter cells | 2 | 4 |
| Number of cell divisions | 1 | 2 |
| Chromosome number | Same as parent cell | Half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell |
| Genetic variation | No | Yes |
Biological Significance of the Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis, Study guide for mitosis and meiosis
The differences between mitosis and meiosis are essential for the proper functioning of organisms. Mitosis is used for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction. Meiosis is used for sexual reproduction. The process of meiosis produces genetic variation, which is essential for evolution.
Genetic variation allows populations of organisms to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Study Guide Structure
To enhance comprehension and retention, the study guide is meticulously organized into distinct sections. These sections are logically arranged to facilitate a progressive understanding of the subject matter.
A comprehensive table of contents is provided at the beginning of the guide, offering a clear overview of the topics covered and their corresponding sections. This enables students to navigate the guide efficiently and locate specific information effortlessly.
Practice Questions and Exercises
To reinforce learning and assess understanding, the study guide incorporates practice questions and exercises. These exercises are carefully designed to cover a range of difficulty levels, catering to diverse learning styles and levels of prior knowledge.
- Multiple-choice questions test students’ comprehension of key concepts and their ability to identify correct answers from a set of options.
- Short-answer questions encourage students to articulate their understanding of specific topics and provide concise explanations.
- Essay questions challenge students to critically analyze the subject matter, synthesize information, and present their insights in a well-organized manner.
FAQ Compilation
What is the key difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four genetically diverse daughter cells.
Why is mitosis important?
Mitosis is essential for growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction.
What is the significance of meiosis?
Meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction, ensuring genetic diversity and the passing on of traits.