Unit 7 chemical names and formulas test review – Embark on a comprehensive journey through Unit 7: Chemical Names and Formulas Test Review. This meticulously crafted guide unravels the intricacies of chemical nomenclature and formulas, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to conquer your upcoming assessment.
Delve into the systematic rules governing ionic and covalent compounds, unraveling the secrets behind their naming conventions. Explore the intricacies of chemical formulas, deciphering the language of chemical composition. Prepare to tackle chemical reactions with aplomb, identifying their diverse types and mastering the art of balancing equations.
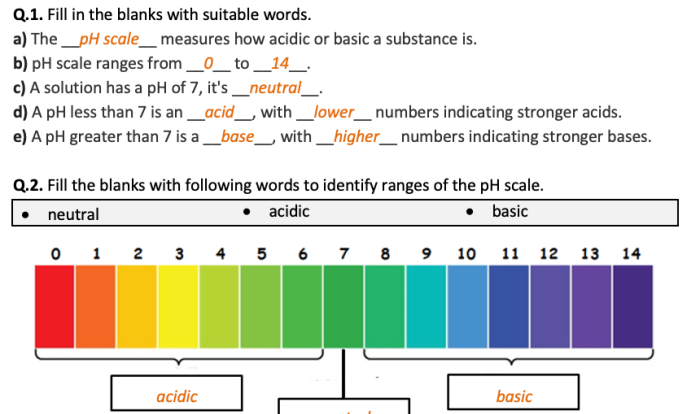
Chemical Nomenclature
Chemical nomenclature is the systematic naming of chemical compounds. It is important for scientists to be able to name compounds accurately so that they can communicate about them clearly. There are two main types of chemical compounds: ionic compounds and covalent compounds.
Ionic Compounds, Unit 7 chemical names and formulas test review
Ionic compounds are formed when a metal loses one or more electrons to a nonmetal. The metal becomes a positively charged ion, called a cation, and the nonmetal becomes a negatively charged ion, called an anion. The two ions are attracted to each other by their opposite charges, forming an ionic bond.
- The rules for naming ionic compounds are as follows:
- The cation is named first, followed by the anion.
- The name of the cation is the same as the name of the metal.
- The name of the anion is the root of the nonmetal’s name, followed by the suffix “-ide”.
For example, the ionic compound NaCl is named sodium chloride. The cation is Na+, which is the sodium ion. The anion is Cl-, which is the chloride ion.
Covalent Compounds
Covalent compounds are formed when two or more nonmetals share electrons. The electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, forming a covalent bond.
- The rules for naming covalent compounds are as follows:
- The first element in the compound is named first, followed by the second element.
- The name of the first element is the same as the name of the element.
- The name of the second element is the root of the element’s name, followed by the suffix “-ide”.
For example, the covalent compound H2O is named water. The first element is hydrogen, and the second element is oxygen. The name of the compound is water.
General Inquiries: Unit 7 Chemical Names And Formulas Test Review
What are the key rules for naming ionic compounds?
Ionic compounds are named using the cation (positive ion) followed by the anion (negative ion). The cation is typically a metal, while the anion is a nonmetal. The name of the cation is the same as the name of the metal, while the name of the anion is derived from the root of the nonmetal’s name, followed by the suffix “-ide”.
How do I write the chemical formula for an ionic compound?
To write the chemical formula for an ionic compound, you must first determine the charges of the ions involved. The charges of the ions can be determined by using the periodic table. Once you know the charges of the ions, you can write the chemical formula by balancing the charges of the ions.
The chemical formula of an ionic compound is written with the cation first, followed by the anion.
What are the different types of chemical reactions?
There are many different types of chemical reactions, but some of the most common types include:
- Combination reactions
- Decomposition reactions
- Single-replacement reactions
- Double-replacement reactions