Chapter 13 genetic engineering chapter vocabulary review – Chapter 13 Genetic Engineering: Chapter Vocabulary Review delves into the fascinating realm of genetic engineering, providing a comprehensive overview of its key concepts, applications, and ethical considerations. This chapter serves as a foundational resource for understanding the intricate world of genetic engineering and its profound implications for science, medicine, and society.
Genetic engineering, the manipulation of an organism’s genetic material, has emerged as a transformative technology with the potential to reshape our understanding of life and revolutionize various industries. This chapter explores the fundamental principles of genetic engineering, its diverse applications in fields such as medicine and agriculture, and the ethical considerations that accompany its use.
1. Genetic Engineering Overview

Genetic engineering is the process of manipulating an organism’s genetic material to change its traits. It involves altering the DNA sequence of an organism to achieve specific outcomes.
Examples of genetic engineering applications include:
- Creating genetically modified crops that are resistant to pests or herbicides
- Developing new medical treatments for diseases such as cancer and cystic fibrosis
- Improving the efficiency of industrial processes by engineering microorganisms
Genetic engineering has the potential to revolutionize various fields and address global challenges such as food security, healthcare, and environmental sustainability.
2. Chapter 13 Vocabulary Review
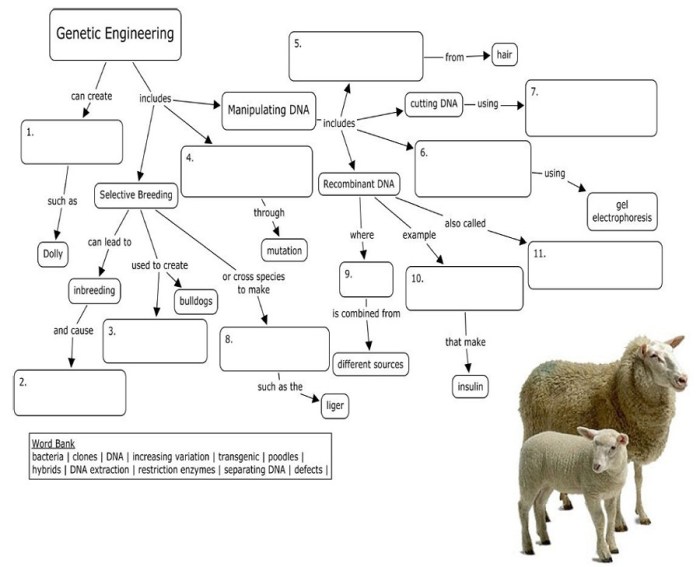
Key Terms:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Allele | Different forms of a gene that occupy the same locus on a chromosome |
| Base pair | Two nucleotides that are complementary and form the building blocks of DNA |
| Chromosome | A thread-like structure in the nucleus of a cell that carries genetic information |
| Gene | A unit of heredity that is responsible for a specific trait |
| Genetic engineering | The process of manipulating an organism’s genetic material to change its traits |
| Genome | The entire genetic material of an organism |
| Recombinant DNA | DNA that is formed by combining DNA from two different sources |
| Transgenic organism | An organism that has been genetically modified by the introduction of foreign DNA |
3. Ethical Considerations
Genetic engineering raises ethical concerns that need to be carefully considered:
- Environmental risks:The release of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) into the environment could have unintended consequences on ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Health risks:The long-term health effects of consuming GMOs or using genetically engineered medical treatments are not fully understood.
- Social justice:Genetic engineering could lead to disparities in access to healthcare and exacerbate social inequalities.
Guidelines and regulations are in place to minimize risks and ensure the ethical use of genetic engineering.
4. Applications in Medicine

Genetic engineering is used in various medical treatments:
- Gene therapy:Replacing or repairing faulty genes to treat genetic diseases
- Pharmacogenomics:Tailoring medical treatments based on an individual’s genetic makeup
- Diagnostics:Identifying genetic markers associated with diseases
Genetic engineering has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by offering personalized treatments and cures for previously untreatable diseases.
5. Applications in Agriculture
Genetic engineering is used to improve crops and livestock:
- Pest and disease resistance:Creating crops that are resistant to pests and diseases, reducing the need for pesticides
- Increased yield:Developing crops with higher yields to meet growing food demands
- Nutritional enhancement:Fortifying crops with essential nutrients to address malnutrition
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) have the potential to improve food security and sustainability, but also raise concerns about their environmental and health impacts.
6. Future Directions: Chapter 13 Genetic Engineering Chapter Vocabulary Review
Genetic engineering is a rapidly evolving field with emerging trends:
- CRISPR-Cas9 technology:A powerful gene-editing tool that enables precise changes to DNA
- Synthetic biology:Designing and creating new biological systems from scratch
- Personalized medicine:Tailoring medical treatments and therapies based on an individual’s genetic profile
Genetic engineering has the potential to shape the future of science and technology, offering solutions to complex global challenges.
FAQs
What is the primary focus of Chapter 13 Genetic Engineering: Chapter Vocabulary Review?
Chapter 13 Genetic Engineering: Chapter Vocabulary Review focuses on providing a comprehensive overview of the key concepts, applications, and ethical considerations related to genetic engineering.
What are the key benefits of genetic engineering?
Genetic engineering offers potential benefits such as improved crop yields, enhanced disease resistance, and the development of new medical treatments.
What are the ethical concerns associated with genetic engineering?
Ethical concerns surrounding genetic engineering include potential environmental impacts, unintended consequences on human health, and the potential for misuse or discrimination.