Label the structures of the thoracic cavity – Labeling the structures of the thoracic cavity is a fundamental aspect of understanding human anatomy and physiology. This cavity houses vital organs, including the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels, and plays a crucial role in respiration, circulation, and other essential bodily functions.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the thoracic cavity, its boundaries, major structures, supporting structures, vasculature, innervation, and common pathologies. By understanding the anatomy and function of the thoracic cavity, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions.
1. Overview of Thoracic Cavity
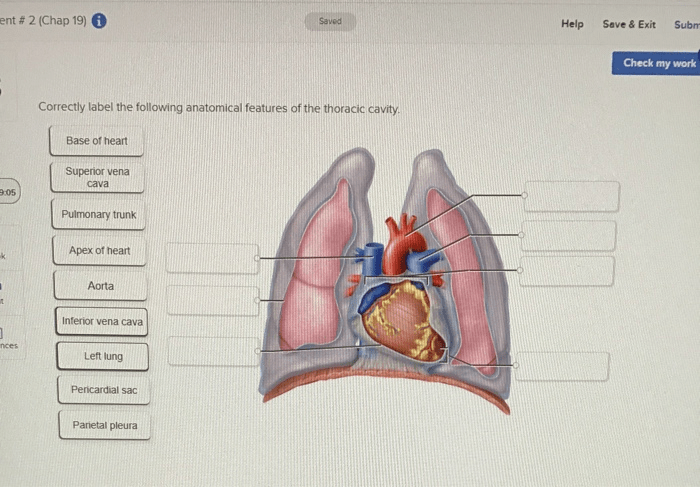
The thoracic cavity is the central cavity of the body, located between the neck and the abdomen. It is bounded superiorly by the thoracic inlet and inferiorly by the diaphragm. The thoracic cavity contains the heart, lungs, and other vital organs.
The thoracic cavity has several important functions. It protects the vital organs from injury, provides space for the lungs to expand and contract, and helps to regulate body temperature.
2. Major Structures of the Thoracic Cavity
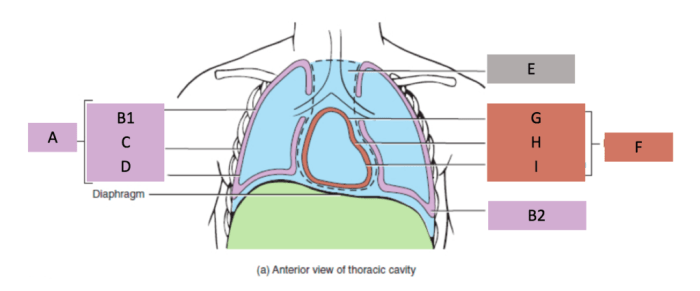
The Heart
- The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
- It is located in the mediastinum, which is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity.
- The heart has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles.
The Lungs
- The lungs are two large, spongy organs that are responsible for gas exchange.
- They are located on either side of the heart.
- Each lung is divided into lobes: the right lung has three lobes and the left lung has two lobes.
The Trachea, Bronchi, and Alveoli, Label the structures of the thoracic cavity
- The trachea is a tube that carries air from the nose and mouth to the lungs.
- The trachea divides into two bronchi, which enter the lungs.
- The bronchi divide into smaller and smaller tubes called bronchioles, which end in tiny air sacs called alveoli.
3. Supporting Structures of the Thoracic Cavity
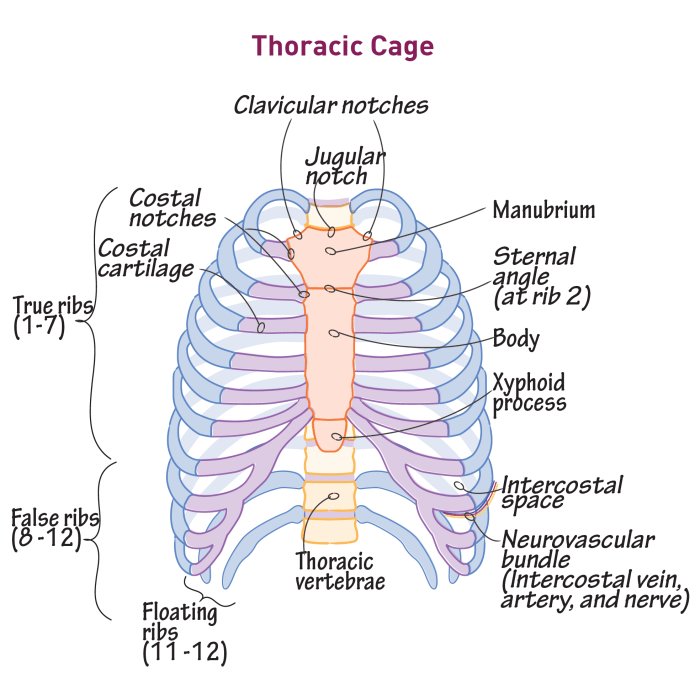
The Thoracic Cage
The thoracic cage is a bony structure that surrounds the thoracic cavity.
It is made up of the ribs, sternum, and vertebrae.
The thoracic cage protects the vital organs from injury and helps to support the weight of the body.
The Diaphragm
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity.
It plays an important role in breathing by contracting and relaxing to change the volume of the thoracic cavity.
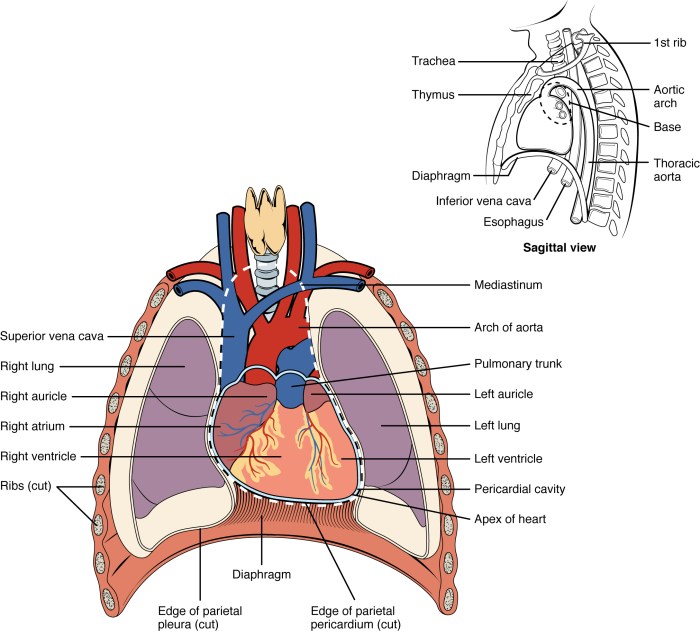
The Mediastinum
The mediastinum is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity.
It contains the heart, great vessels, trachea, esophagus, and other structures.
The mediastinum is divided into several compartments by fascial layers.
4. Vasculature and Innervation of the Thoracic Cavity
Major Blood Vessels
- The aorta is the largest artery in the body.
- It carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
- The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
- The pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
Lymphatic Drainage
The thoracic cavity is drained by a network of lymphatic vessels.
These vessels collect excess fluid and waste products from the tissues of the thoracic cavity.
The lymphatic vessels empty into the thoracic duct, which drains into the bloodstream.
Innervation
The thoracic cavity is innervated by the vagus nerve, phrenic nerve, and sympathetic nerves.
These nerves control the function of the heart, lungs, and other organs in the thoracic cavity.
5. Pathologies of the Thoracic Cavity: Label The Structures Of The Thoracic Cavity
Common Pathologies
- Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs.
- Pleural effusion is a collection of fluid in the pleural space.
- Pneumothorax is a collapse of the lung.
- Lung cancer is a malignant tumor of the lung.
Symptoms and Treatment
The symptoms of thoracic cavity pathologies vary depending on the specific pathology.
Common symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and cough.
Treatment for thoracic cavity pathologies also varies depending on the specific pathology.
Treatment may include antibiotics, surgery, or radiation therapy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the boundaries of the thoracic cavity?
The thoracic cavity is bounded superiorly by the thoracic inlet, inferiorly by the diaphragm, anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages, posteriorly by the thoracic vertebrae, and laterally by the ribs and intercostal muscles.
What are the major structures of the thoracic cavity?
The major structures of the thoracic cavity include the heart, lungs, trachea, bronchi, esophagus, and thymus gland.
What are the supporting structures of the thoracic cavity?
The supporting structures of the thoracic cavity include the thoracic cage, diaphragm, and mediastinum.
What are the major blood vessels of the thoracic cavity?
The major blood vessels of the thoracic cavity include the aorta, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, and superior and inferior vena cava.