The membrane transport concept map answer key unlocks a gateway to understanding the intricate mechanisms of cellular movement. This essential tool provides a comprehensive roadmap, revealing the key components, relationships, and factors that govern the transport of molecules across biological membranes.
Dive into this illuminating guide to unravel the complexities of membrane transport, empowering you with a deeper comprehension of cellular processes.
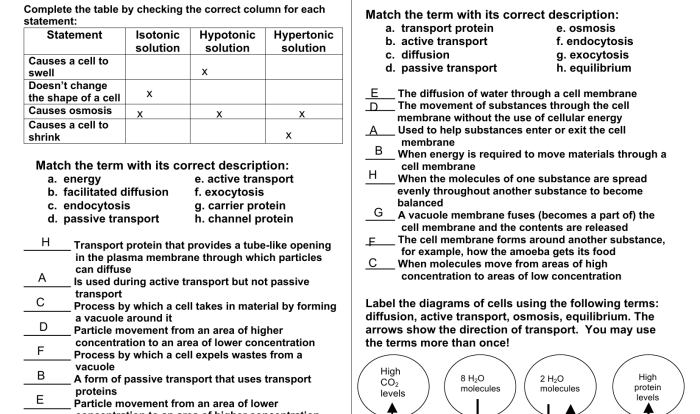
1. Membrane Transport Concept Map
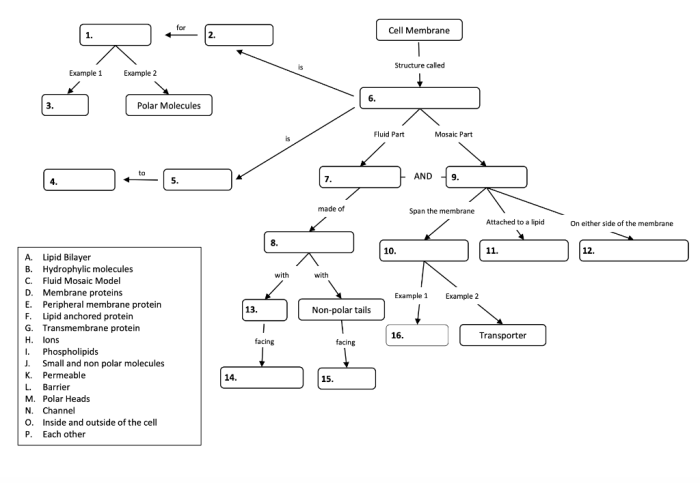
A concept map for membrane transport provides a visual representation of the key concepts and their relationships in membrane transport. It helps organize and connect information, making it easier to understand the complex processes involved in membrane transport.
The key components of a concept map for membrane transport include:
- Membrane transport: The movement of molecules across a biological membrane.
- Types of membrane transport: Active transport, passive transport, and facilitated diffusion.
- Factors affecting membrane transport: Concentration gradient, membrane permeability, and temperature.
- Applications of membrane transport: Osmosis, drug delivery, and water purification.
The relationships between the different components of a concept map for membrane transport can be shown using arrows, lines, or other visual cues. For example, arrows can be used to indicate the direction of movement of molecules across a membrane, and lines can be used to connect different types of membrane transport to their corresponding mechanisms.
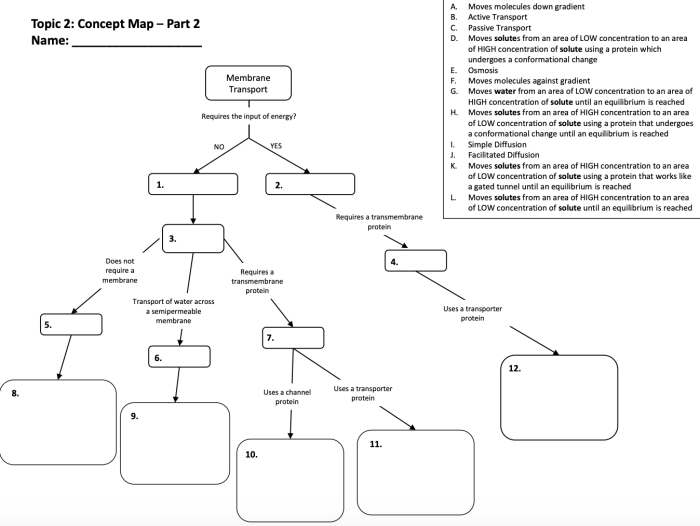
2. Types of Membrane Transport
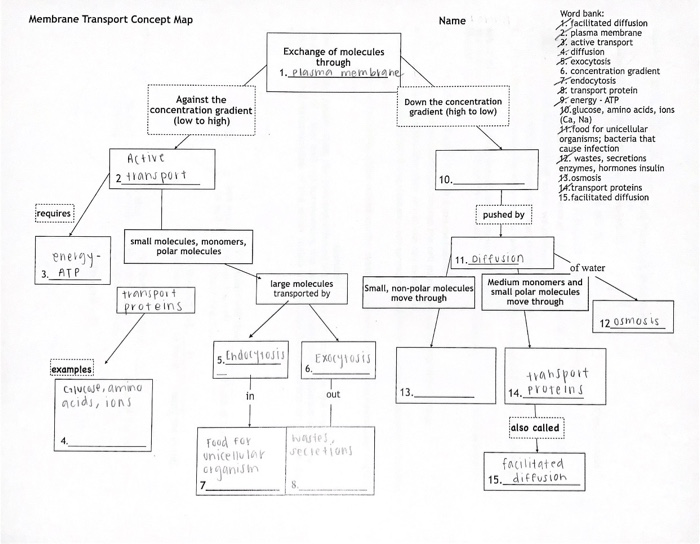
There are three main types of membrane transport:
- Active transport: The movement of molecules across a membrane against a concentration gradient, requiring energy input.
- Passive transport: The movement of molecules across a membrane down a concentration gradient, not requiring energy input.
- Facilitated diffusion: The movement of molecules across a membrane with the assistance of a carrier protein, down a concentration gradient.
Active transport is used to move molecules against a concentration gradient, such as the movement of ions across a cell membrane. Passive transport is used to move molecules down a concentration gradient, such as the movement of water across a cell membrane.
Facilitated diffusion is used to move molecules across a membrane with the assistance of a carrier protein, such as the movement of glucose across a cell membrane.
3. Factors Affecting Membrane Transport: Membrane Transport Concept Map Answer Key
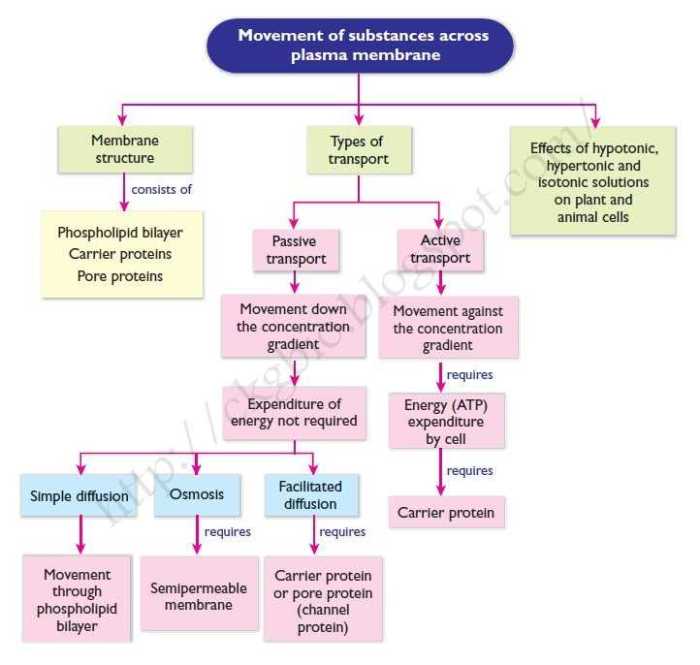
The rate of membrane transport is affected by several factors, including:
- Concentration gradient: The difference in concentration of a molecule across a membrane.
- Membrane permeability: The ability of a membrane to allow molecules to pass through.
- Temperature: The temperature of the membrane.
The concentration gradient is the most important factor affecting membrane transport. The greater the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of membrane transport. The membrane permeability is also an important factor, as it determines how easily molecules can pass through the membrane.
The temperature of the membrane can also affect the rate of membrane transport, as higher temperatures can increase the fluidity of the membrane and make it more permeable to molecules.
4. Applications of Membrane Transport
Membrane transport has a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Osmosis: The movement of water across a semipermeable membrane, used in water purification and desalination.
- Drug delivery: The use of membrane transport to deliver drugs to specific cells or tissues.
- Water purification: The use of membrane transport to remove impurities from water.
Osmosis is used to purify water by removing impurities, such as salt and bacteria. Drug delivery uses membrane transport to deliver drugs to specific cells or tissues, which can improve the effectiveness of the drug and reduce side effects. Water purification uses membrane transport to remove impurities from water, such as salt and bacteria, making it safe for drinking.
5. Interactive Resources
There are a number of interactive resources available for learning about membrane transport, including:
- Simulations: Simulations that allow users to explore the different types of membrane transport and the factors that affect them.
- Videos: Videos that explain the different types of membrane transport and their applications.
- Other resources: Other resources, such as articles and quizzes, that can help users learn about membrane transport.
These resources can be used to enhance understanding of membrane transport and to make learning more engaging and interactive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of a membrane transport concept map?
A membrane transport concept map is a visual representation that organizes and interconnects key concepts related to membrane transport, providing a comprehensive overview of the topic.
How can I use the membrane transport concept map answer key?
The answer key provides explanations and elaborations for the concepts presented in the concept map, aiding in the understanding and retention of membrane transport mechanisms.
What are the different types of membrane transport?
Membrane transport encompasses passive transport, where molecules move down a concentration gradient without energy input, and active transport, where molecules are transported against a concentration gradient with energy expenditure.